LLMs for Dummies - Walkthrough Guide and Glossary
A Small glossary of LLM terms for beginners:
Transformer : The transformer model architecture enables the LLM to understand and recognize the relationships and connections between words and concepts using a self-attention mechanism.
Large Language Model (LLM) : is a deep learning algorithm that can perform a variety of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. Large language models use transformer models and are trained using massive datasets — hence, large. This enables them to recognize, translate, predict, or generate text or other content.
By Renee Shaw from Medium
Images credit: author made in excallidraw
A Transformer is a technique used in AI for processing language. An LLM is a big AI model for language tasks, often built using the Transformer technique.
Interface : is the user-friendly platform that allows beginners to interact with a Large Language Model. It provides easy access to the model's capabilities, making tasks like generating text or answering questions straightforward. Essentially, it's the simplified bridge between the user and the LLM's linguistic prowess.
Inference : In the context of Large Language Models, inference refers to the model's ability to draw conclusions, make predictions, or generate responses based on the input it receives. It's like the model's way of making educated guesses or providing useful information by understanding and processing the data it's given. In simpler terms, inference is how the Large Language Model uses its knowledge to generate relevant and meaningful output in response to user queries or tasks.
Supervised Learning : is a training approach for Large Language Models where the model learns from labelled examples. In simpler terms, it's like teaching the model by providing it with input-output pairs, helping it understand the patterns and relationships in the data. The "supervisor" guides the model during training, making it akin to a learning process with a teacher. Once trained, the model can apply this knowledge to generate accurate responses or predictions when given new, unseen input.
Unsupervised Learning (heeeyo) : is a type of machine learning where a Large Language Model (LLM) learns patterns and structures in data without explicit guidance or labelled examples. In the context of LLMs, it means the model can explore and understand language on its own, without being explicitly told what each piece of text means. It's like the LLM discovers relationships and insights within the vast amount of language data it processes, allowing it to develop a deeper understanding of the nuances and context of natural language.
By Renee Shaw from Medium
Images credit: author made in excallidraw
Reinforcement Learning : is a type of machine learning where a Large Language Model (LLM) learns by receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. It's akin to training a model through a trial-and-error process. In the case of LLMs, reinforcement learning helps the model improve its language generation by adjusting its responses based on positive or negative feedback. Essentially, it's like the LLM learning to produce better results over time by understanding which language outputs are more favourable or accurate. Neural Network — Designed to work a bit like a human brain. It consists of lots of small units (like brain cells) that work together to process information and solve problems.
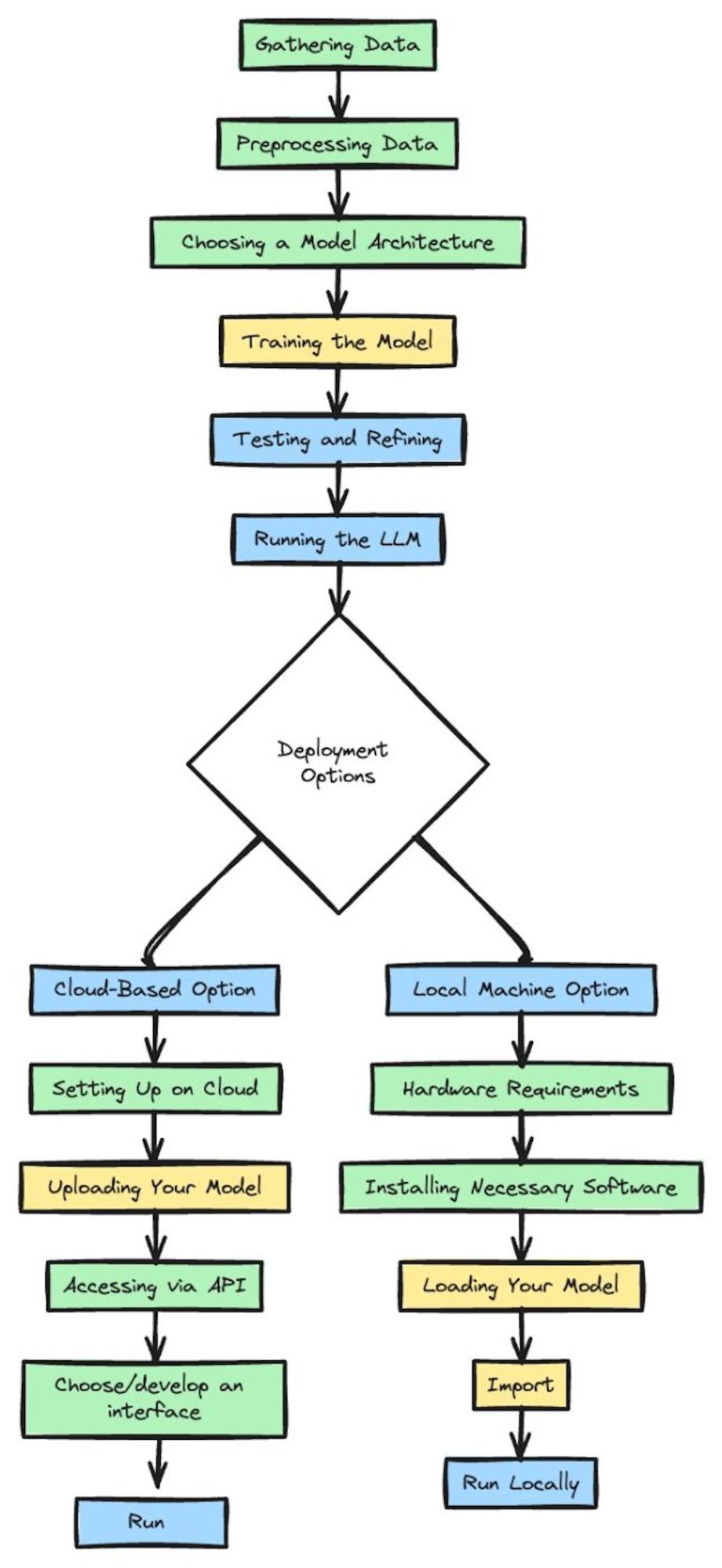
Creating an LLM :
Gathering your Data :
Begin by gathering a diverse range of text data, which may encompass books, online articles, or information from databases. The broader the spectrum of your data, the more proficient your LLM will become in comprehending various facets of language.
Explore Kaggle for excellent datasets suitable for machine learning and data science projects. Jeremy Howard, an accomplished Kaggle grandmaster from Australia, is a valuable resource worth checking out.
Additionally, GitHub frequently serves as a repository for datasets shared by researchers and developers, making it a reliable platform for your search.
Clean your data :
This step is about fixing errors, removing parts that aren’t useful, and organising them so your AI can learn from them effectively.
Choosing a Model Architecture :
The model architecture serves as the framework or blueprint, outlining how the AI processes information. Specifically designed for sequential data like text, the Transformer architecture is crafted to excel in understanding the contextual intricacies within the data.
Training the Model :
Now, give your AI model the prepared data to start learning the details of language. Keep in mind that training can take a while, especially if you have a large amount of data.
Testing and Refining :
After the training, evaluate how well your AI understands and generates language. Depending on the results, you might need to adjust and retrain to enhance its performance.
By Renee Shaw from Medium
Images credit: author made in excallidraw
Running the LLM :
Now, how do you run the beast?
Rather than starting from scratch to create an LLM, you can utilise Hugging Face to tap into models already trained on massive datasets. These models can be executed either through their cloud service or downloaded for local use on your machine.